Dubbo基础---RPC是如何实现的
RPC(Remote Procedure Call Protocol)是一种远程调用协议, 允许像调用本地服务那样调用远程其它服务,即实现跨进程交互。
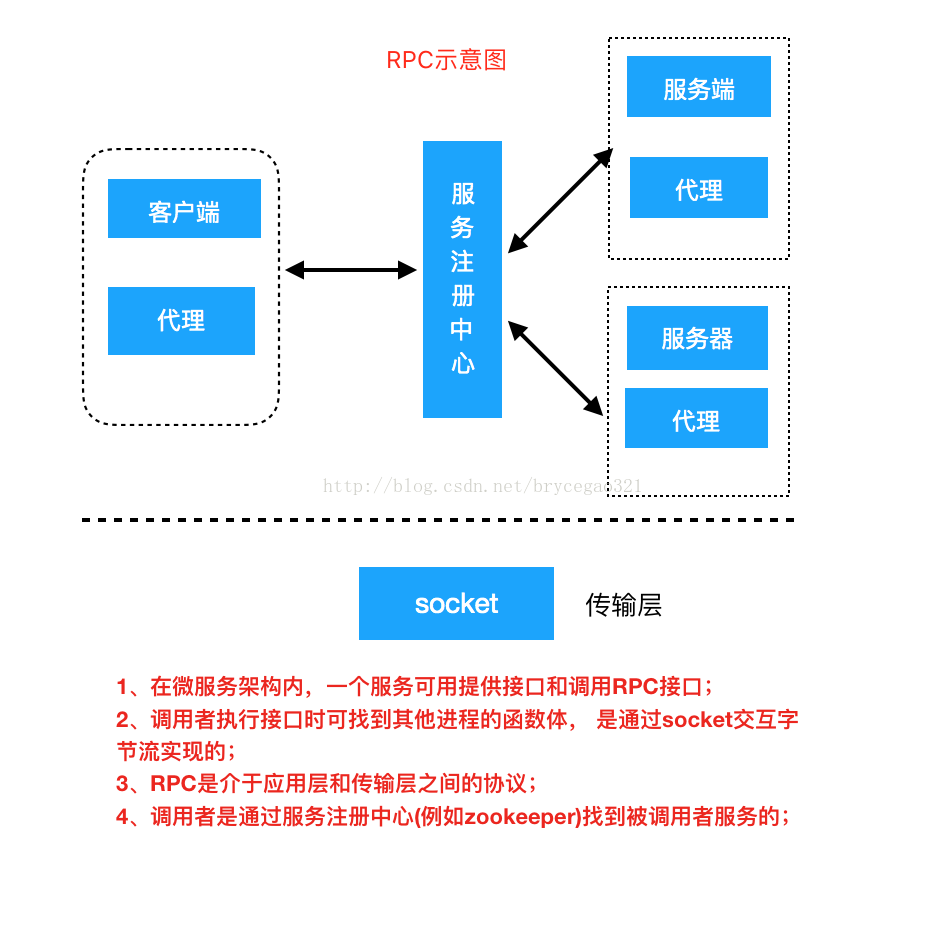
如上图所示:
1、 客户端是指调用者, 服务端是指被调用者; 在现在流行的微服务框架内, 客户端也可以是Web服务, 既提供接口也调用其它服务的接口;
2、服务注册中心的作用负载均衡,记录活着的服务并导流到真正的服务进程;
3、客户端(也可以成为服务消费者)通过服务注册中心找到真正的服务端(服务提供者);
在讲RPC前先看个Java特性, 即Java对象和字节流互相转换, 这是RPC的基础!!!
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "Tom");
map.put("age", "20");
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(map); //将Java对象转换成流
byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); //将map对象转换成字节流
System.out.println("我就是map对象的字节流:");
System.out.println(new String(bytes, "utf-8"));
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
Map<String, String> objMap = (Map<String, String>)objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println("字节流转换成map对象,大小:" + objMap.size());
执行后输出:
我就是map对象的字节流: ��srjava.util.HashMap���`�F loadFactorI thresholdxp?@tnametTomtaget20x 字节流转换成map对象,大小:2
记住ObjectInputStream和ObjectOutputStream类, 它可以将map对象转换成字节流, 也可以将字节流转换为map对象。 Java各个进程之间可以通过socket交互字节流, 从而实现调用API的目的。
使用一个进程模拟找到函数体:
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
Method method = ImitateRpc.class.getMethod("callRemote", String.class); //模拟RPC调用的API
//模拟客户端发送数据
outputStream.writeUTF(ImitateRpc.class.getName()); //接口类名
outputStream.writeUTF(method.getName()); //方法名称
outputStream.writeObject(method.getParameterTypes()); //方法参数类型
Object[] args = new Object[1];
args[0] = "Tom";
outputStream.writeObject(args); //方法参数
/**
* 此处省略了客户端发送字节流到服务端和服务端接收字节流的过程
*/
//模拟服务端接收到数据
ByteArrayInputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream serverInputStreamp = new ObjectInputStream(inputStream);
String serviceName = serverInputStreamp.readUTF(); //接口类
String methodName = serverInputStreamp.readUTF();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = (Class<?>[]) serverInputStreamp.readObject();
Object[] arguments = (Object[]) serverInputStreamp.readObject();
Class svrClass = ImitateRpcImpl.class; //实现类
Method svrMethod = svrClass.getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
Object result = svrMethod.invoke(svrClass.newInstance(), arguments);
从上面代码可以看出客户端在执行API时,将接口类、方法名、参数类型、参数转换成字节流outputStream, 服务端使用inputStream解析字节流并执行函数体(PS:这里省略了客户端/服务器通讯的代码)。
在上面代码基础上添加socket通讯就是完整的RPC例子了:
服务端代码要监听端口, 拿到数据后解析出接口名、方法名、参数类型、参数后执行函数体,并将返回值回写socket里。
public class RegistryCenter implements RegistryService {
private final ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,
200, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>(1024));
//参数SpringCloud做法,使用服务名称作为主键
private final HashMap<String, ServiceInfo> services = new HashMap<>(); //注册服务的信息
private int port;
class ServiceInfo {
Class service; //接口
Class impl;
String ip;
int port;
}
public RegistryCenter(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void registerService(Class service, Class impl, String ip, int port) {
ServiceInfo info = new ServiceInfo();
info.service = service;
info.impl = impl;
info.ip = ip;
info.port = port;
services.put(service.getName(), info);
}
@Override
public boolean start() throws IOException{
if (services.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
ServerSocket server = null;
try {
server = new ServerSocket();
server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("start server");
while (true) {
executorService.execute(new ProviderTask(server.accept()));
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (server != null) {
server.close();
}
}
return true;
}
//生产者(接口实现者)的逻辑, 基于短连接
class ProviderTask implements Runnable {
Socket server = null;
public ProviderTask(Socket socket) {
server = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
ObjectInputStream input = null;
ObjectOutputStream output = null;
try {
//从socket字节流转换成要调用的API
input = new ObjectInputStream(server.getInputStream());
String serviceName = input.readUTF();
String methodName = input.readUTF();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = (Class<?>[])input.readObject();
Object[] arguments = (Object[]) input.readObject();
ServiceInfo info = services.get(serviceName);
if (info == null) {
throw new Exception("没有该服务" + serviceName);
}
Class clz = info.impl;
Method method = clz.getMethod(methodName, paramTypes); //找到方法
Object result = method.invoke(clz.newInstance(), arguments); //执行函数
output = new ObjectOutputStream(server.getOutputStream());
output.writeObject(result);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放资源
if (output != null) {
try {
output.close();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (input != null) {
try {
input.close();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (server != null) {
try {
server.close();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
客户端代码转换API信息为字节流并发送到服务端, 然后监听返回值并转换为Java对象。
public class RpcHelloClient {
/**
* 获取远程服务的代理对象
* @param service, 接口
* @param addr,远程服务运行端口
* @return 对象
*/
public static <T> T getRpcProxyObj(Class<?> service, InetSocketAddress addr) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(service.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{service},
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Socket socket = null;
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = null;
ObjectInputStream inputStream = null;
try {
socket = new Socket();
socket.connect(addr);
//发送字节流到远程服务
outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
outputStream.writeUTF(service.getName());
outputStream.writeUTF(method.getName());
outputStream.writeObject(method.getParameterTypes());
outputStream.writeObject(args);
//阻塞等待返回
inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
Object obj = inputStream.readObject();
return obj; //类对象
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
if (outputStream != null) {
outputStream.close();
}
}
return null;
}
});
}
}
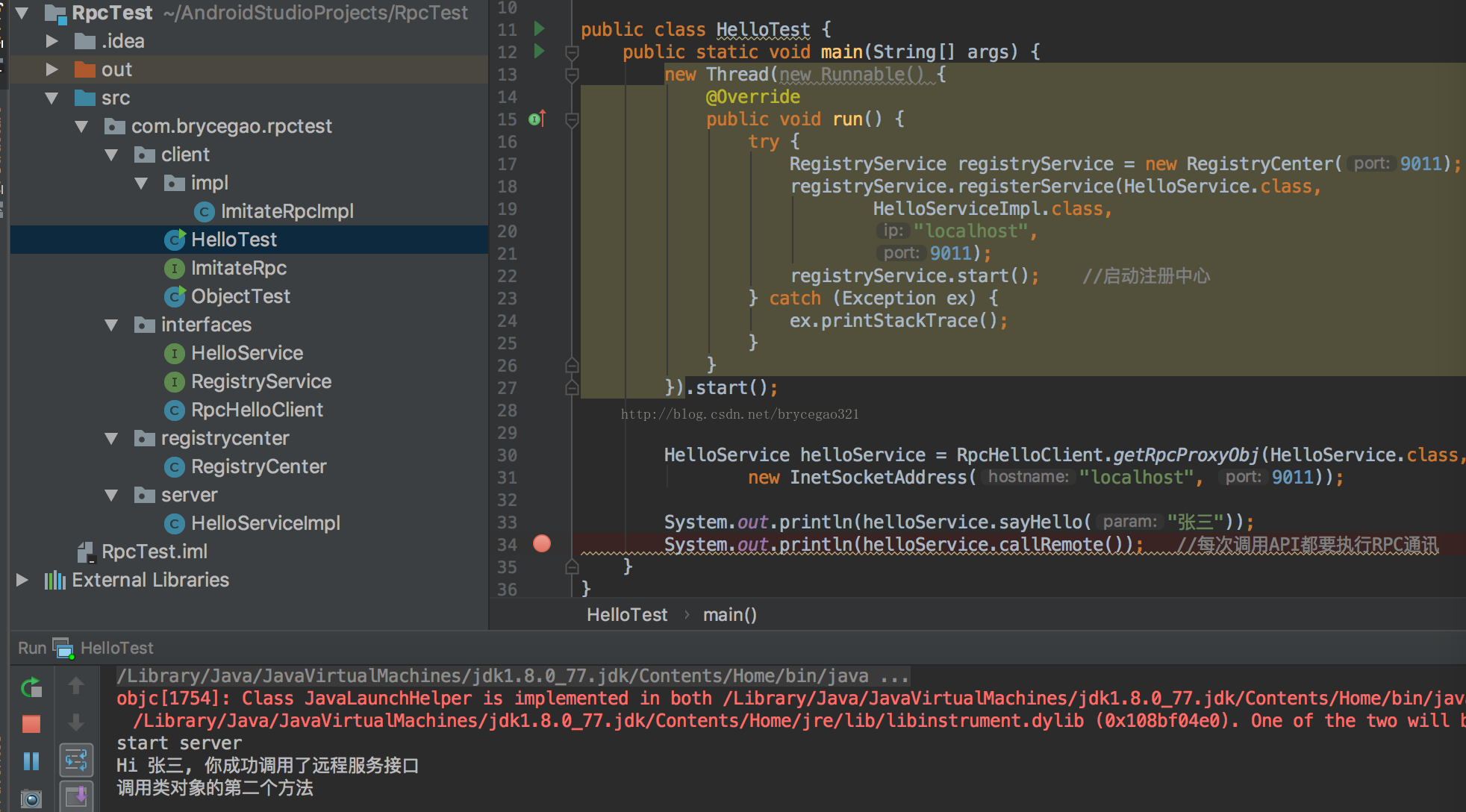
本机运行一下:
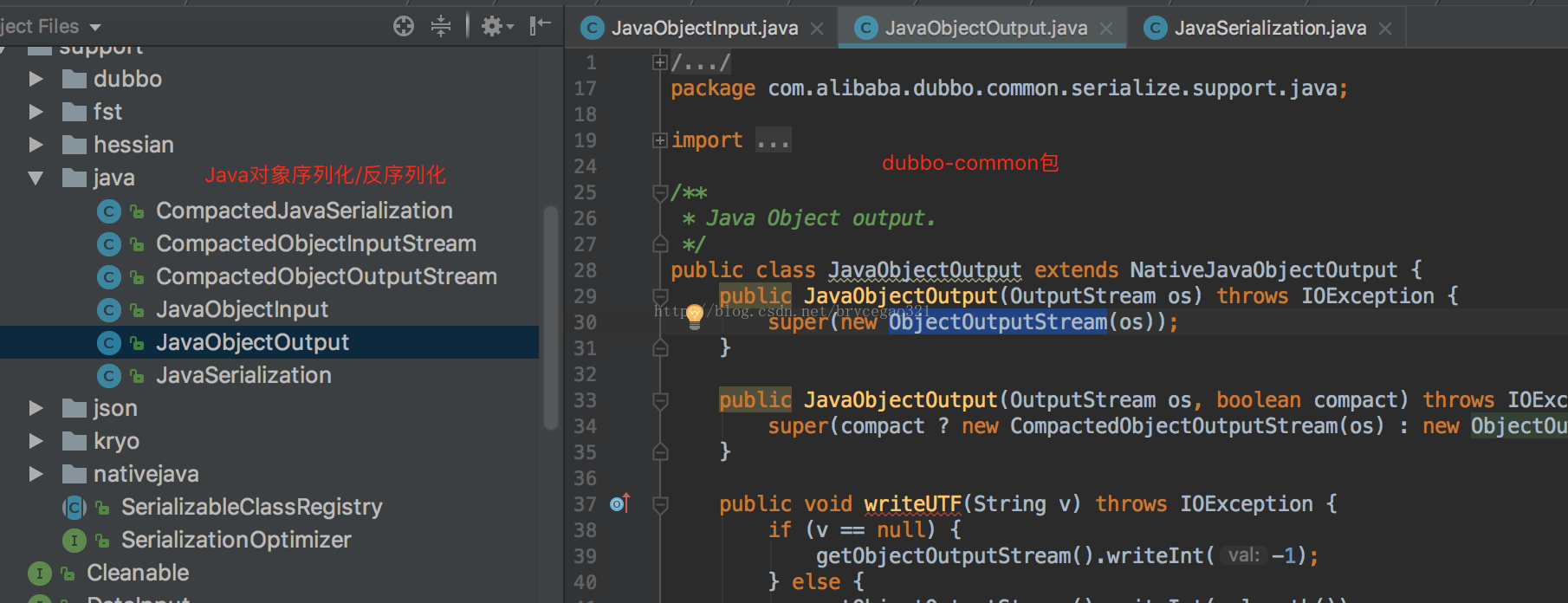
再看看Dubbo源码是怎么转换Java对象的, 在dubbo.io地址里下载源码,搜索ObjectInputStream或者ObjectOutputStream, 在dubbo-common里找到了这几个类(功能是Java对象/字节流之间互转)。
本示例是基于短连接的, 每执行一次RPC调用都要重连服务端;而Dubbo是基于长连接的。
完整代码: http://download.csdn.net/download/brycegao321/10246971
声明:该文观点仅代表作者本人,牛骨文系教育信息发布平台,牛骨文仅提供信息存储空间服务。