nltk中的FreqDist,ConditionalFreqDist和Bigram
1. FreqDist的使用:接受参数words后, 会统计words中每个word的频数,并返回一个字典,key是word,value是word在words中出现的频数。
sentences = "异响严重,副驾门异响,不知不觉就到了3000公里首保"
sentences2 = "我的小悦也有异响了!"
words = jieba.lcut(sentences)
words1 = jieba.lcut(sentences2)
from nltk.probability import FreqDist,ConditionalFreqDist
a = FreqDist(words)
print(a)
<FreqDist with 13 samples and 14 outcomes>
a
Out[94]:
FreqDist({",": 1,
"3000": 1,
"不知不觉": 1,
"严重": 1,
"了": 1,
"公里": 1,
"到": 1,
"副": 1,
"就": 1,
"异响": 2,
"首保": 1,
"驾门": 1,
",": 1})
2. ConditionalFreqDist的使用
(1)条件频率分布需要处理的是配对列表,每对的形式是(条件,事件),conditions()函数会返回这里的条件
b = ConditionalFreqDist()
for word in words:
b["pos"][word] += 1
for word in words1:
b["neg"][word] += 1
b
Out[151]:
ConditionalFreqDist(nltk.probability.FreqDist,
{"neg": FreqDist({"也": 1,
"了": 1,
"小悦": 1,
"异响": 1,
"我": 1,
"有": 1,
"的": 1,
"!": 1}),
"pos": FreqDist({",": 1,
"3000": 1,
"不知不觉": 1,
"严重": 1,
"了": 1,
"公里": 1,
"到": 1,
"副": 1,
"就": 1,
"异响": 2,
"首保": 1,
"驾门": 1,
",": 1})})b.conditions() Out[152]: ["pos", "neg"]
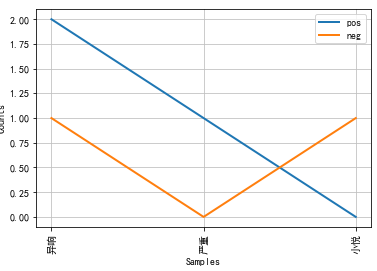
b["pos"].N() Out[172]: 14(2)b.tabulate(conditions, samples)会返回对应条件中事件发生的频率
genres = ["words","words1"]
modals = ["异响","严重","首保"]
b.tabulate(conditions=genres, samples=modals)
异响 严重 首保
words 2 1 1
words1 2 1 1 (3)b.plot(conditions, samples)
import matplotlib #rcParams改变全局字体 matplotlib.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei" b.plot(conditions=genres, samples=modals)
3. Bigram:把双词搭配(bigrams)作为特征
from nltk.collocations import BigramCollocationFinder
from nltk.metrics import BigramAssocMeasures
def bag_of_words(words):
return dict([(word,True) for word in words])
def bigram(words, score_fn=BigramAssocMeasures.chi_sq, n=1000):
bigram_finder = BigramCollocationFinder.from_words(words)
bigrams = bigram_finder.nbest(score_fn, n)
print(bigrams)
newBigrams = [u+v for (u,v) in bigrams]
return bag_of_words(newBigrams)
bigram(words)
[(",", "不知不觉"), ("3000", "公里"), ("不知不觉", "就"), ("严重", ","), ("了", "3000"), ("公里", "首保"), ("到", "了"), ("副", "驾门"), ("就", "到"), (",", "副"), ("异响", ","), ("异响", "严重"), ("驾门", "异响")]
Out[168]:
{",不知不觉": True,
"3000公里": True,
"不知不觉就": True,
"严重,": True,
"了3000": True,
"公里首保": True,
"到了": True,
"副驾门": True,
"就到": True,
"异响,": True,
"异响严重": True,
"驾门异响": True,
",副": True}
声明:该文观点仅代表作者本人,牛骨文系教育信息发布平台,牛骨文仅提供信息存储空间服务。
- 上一篇: 使用Windbg简单排查线程 CPU 100%的方法
- 下一篇: js中记录某个按钮的点击次数

