【Linux学习笔记】获取文件属性 — stat()、fstat()、lstat()小结
Linux是基于文件的操作系统,一切皆文件。下面就详细的整理一下关于Linux文件属性的内容。
一、文件属性函数
系统提供了3个获取文件属性的函数,分别是:stat()、fstat()、lstat()。
1、函数原型
头文件包含:
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf); int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);注意:
(1) stat() 和 lstat() 都是通过文件路径和文件名访问到文件,然后把文件属性放到 struct stat *buf中;而 fstat() 是通过文件描述符得到文件的属性。
(2) 文件本身没有什么权限限制,但是文件的上层目录必须有访问权限才能获取到文件的属性。
(3) 当文件是符号链接时,lstat() 返回的是该符号链接本身的信息;而 stat() 返回的是该该符号链接指向的文件的信息。
2、文件属性结构体在获取文件属性的时候,使用到了系统定义的文件属性结构体,结构体定义在<sys/stat.h>中,原型如下:
struct stat { dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */ mode_t st_mode; /* protection */ nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */ uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */ gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */ dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */ off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */ blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */ blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */ time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ };
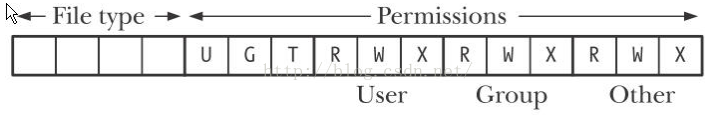
其中,st_mode成员描述了文件的 类型 和 权限 两个属性。st_mode是32位的整型变量,目前只使用了该变量的低16位。
// 八进制,过滤出前四位表示的文件类型
S_IFMT 0170000 bit mask for the file type bit fields
// bit12 ~ bit15
S_IFSOCK 0140000 socket
S_IFLNK 0120000 symbolic link
S_IFREG 0100000 regular file
S_IFBLK 0060000 block device
S_IFDIR 0040000 directory
S_IFCHR 0020000 character device
S_IFIFO 0010000 FIFO
// 特殊属性,分别为set-user-ID位、set-group-ID位和sticky位
S_ISUID 0004000 set UID bit
S_ISGID 0002000 set-group-ID bit (see below)
S_ISVTX 0001000 sticky bit (see below)
// Permission属性区域的bit0~bit8,即st_mode字段的最低9位,代表文件的许可权限,
// 标识了文件所有者(owner)、组用户(group)、其他用户(other)的
// 读(r)、写(w)、执行(x)权限。S_IRWXU 00700 mask for file owner permissions
S_IRUSR 00400 owner has read permission
S_IWUSR 00200 owner has write permission
S_IXUSR 00100 owner has execute permission
S_IRWXG 00070 mask for group permissions
S_IRGRP 00040 group has read permission
S_IWGRP 00020 group has write permission
S_IXGRP 00010 group has execute permission
S_IRWXO 00007 mask for permissions for others (not in group)
S_IROTH 00004 others have read permission
S_IWOTH 00002 others have write permission
S_IXOTH 00001 others have execute permission
在最后面的示例代码中,会通过 st_mode 成员来判断文件的类型。
3、返回值及错误
老规矩:
成功返回0,错误返回-1,并设置errno。
错误返回:
1、ENOENT 参数file_name 指定的文件不存在
2、ENOTDIR 路径中的目录存在但却非真正的目录
3、ELOOP 欲打开的文件有过多符号连接问题, 上限为16 符号连接
4、EFAULT 参数buf 为无效指针, 指向无法存在的内存空间
5、EACCESS 存取文件时被拒绝
6、ENOMEM 核心内存不足
7、ENAMETOOLONG 参数file_name 的路径名称太长
二、示例
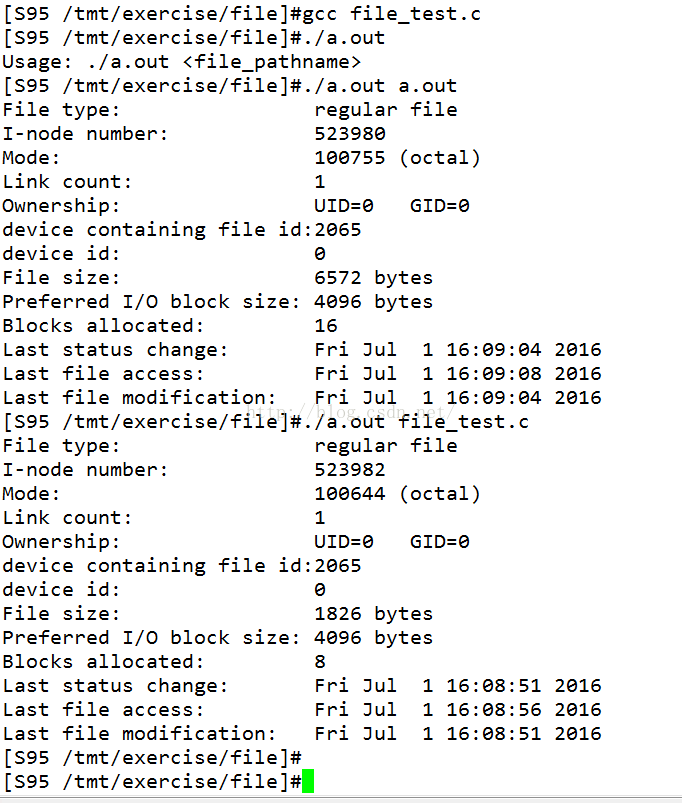
/* file stat example */ #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> int main(int argc, char **argv){ struct stat st; if(argc != 2){ fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <file_pathname> ", argv[0]); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } if(stat(argv[1], &st) == -1){ perror("stat"); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); } printf("File type: "); switch(st.st_mode & S_IFMT){ case S_IFBLK: printf("block device "); break; case S_IFCHR: printf("character device "); break; case S_IFDIR: printf("directory "); break; case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO/pipe "); break; case S_IFLNK: printf("symlink "); break; case S_IFREG: printf("regular file "); break; case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket "); break; default: printf("unknown? "); break; } printf("I-node number: %ld ", (long) st.st_ino); printf("Mode: %lo (octal) ", (unsigned long) st.st_mode); printf("Link count: %ld ", (long) st.st_nlink); printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld ", (long) st.st_uid, (long) st.st_gid); printf("device containing file id:%ld ", (long) st.st_dev); printf("device id: %ld ", (long) st.st_rdev); printf("File size: %lld bytes ", (long long) st.st_size); printf("Preferred I/O block size: %ld bytes ", (long) st.st_blksize); printf("Blocks allocated: %lld ", (long long) st.st_blocks); printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&st.st_ctime)); printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&st.st_atime)); printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&st.st_mtime)); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); }
三、运行结果
- 上一篇: fstat、stat和lstat 区别(转)
- 下一篇: stat、fstat和lstat函数