д»ҘеҸҰеӨ–дёҖдёӘж»ӨжіўеҷЁиҖҢиЁҖ----еқҮеҖјж»ӨжіўеҷЁ, е°ұжҳҜиҜҙжҹҗеғҸзҙ зҡ„йўңиүІ, з”ұд»Ҙе…¶дёәдёӯеҝғзҡ„д№қе®«ж јзҡ„еғҸзҙ е№іеқҮеҖјжқҘеҶіе®ҡ. еңЁиҝҷдёӘеҹәзЎҖдёҠеҸҲеҸ‘еұ•жҲҗдәҶеёҰжқғзҡ„вҖңе№іеқҮвҖқж»ӨжіўеҷЁ, иҝҷйҮҢзҡ„й«ҳж–Ҝе№іж»‘жҲ–иҖ…иҜҙж»ӨжіўеҷЁе°ұжҳҜиҝҷж ·дёҖз§ҚеёҰжқғпјҲйҖҡеёёжҲ‘们и®Өдёәи·қзҰ»иҰҒд»Јжӣҝзҡ„зӮ№еғҸзҙ зҡ„дҪңз”ЁеӨ§дёҖдәӣпјүзҡ„вҖңе№іеқҮвҖқж»ӨжіўеҷЁ. йӮЈд№ҲиҝҷдәӣжқғйҮҚеҰӮдҪ•еҲҶеёғе‘ў? жҲ‘们е…ҲжқҘзңӢеҮ дёӘз»Ҹе…ёзҡ„жЁЎжқҝдҫӢеӯҗ:
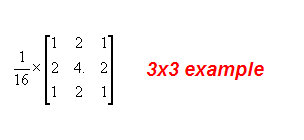
е°қиҜ•дәҶдҪҝз”Ёиҝҷдәӣж»ӨжіўеҷЁеҜ№жҲ‘们еҺҹжқҘзҡ„еӣҫиҝӣиЎҢж“ҚдҪң, еҫ—еҲ°дәҶиҝҷж ·зҡ„дёҖз»„з»“жһң:
еҺҹеӣҫ:

3x3 й«ҳж–Ҝж»ӨжіўеӨ„зҗҶеҗҺ:

5x5 й«ҳж–ҜеӨ„зҗҶеҗҺ:

В
еҚ•зәҜд»Һж•ҲжһңжқҘзңӢ, дёӨдёӘжЁЎжқҝйғҪиө·еҲ°дәҶе№іж»‘зҡ„дҪңз”Ё, еҸӘжҳҜзЁӢеәҰжңүж·ұжө…зҡ„еҢәеҲҶ. йӮЈд№Ҳд»ҺзҗҶи®әдёҠжқҘиҜҙдёәд»Җд№ҲиғҪиө·еҲ°е№іж»‘зҡ„дҪңз”Ёе‘ў? еҫҲжҳҫ然, еғҸзҙ зҡ„йўңиүІдёҚд»…з”ұиҮӘиә«еҶіе®ҡдәҶ, еҗҢж—¶жңүе…¶е‘Ёеӣҙзҡ„еғҸзҙ еҠ жқғеҶіе®ҡ, е®ўи§ӮдёҠеҮҸе°ҸдәҶе’Ңе‘ЁеӣҙеғҸзҙ зҡ„е·®ејӮ.еҗҢж—¶иҝҷдәӣжқғйҮҚзҡ„и®ҫе®ҡж»Ўи¶ідәҶи¶Ҡиҝ‘жқғйҮҚи¶ҠеӨ§зҡ„规еҫӢ. д»ҺзҗҶи®әжқҘи®І, иҝҷдәӣжқғйҮҚзҡ„еҲҶеёғж»Ўи¶ідәҶи‘—еҗҚзҡ„жүҖи°“й«ҳж–ҜеҲҶеёғ:
иҝҷе°ұжҳҜ1з»ҙзҡ„и®Ўз®—е…¬ејҸпјҡ
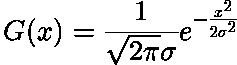
В В
иҝҷе°ұжҳҜ2з»ҙзҡ„и®Ўз®—е…¬ејҸпјҡ
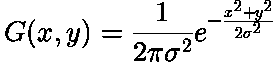
В
x, yиЎЁзӨәзҡ„е°ұжҳҜеҪ“еүҚзӮ№еҲ°еҜ№еә”зӮ№зҡ„и·қзҰ», иҖҢйӮЈдәӣе…·дҪ“зҡ„жЁЎжқҝе°ұжҳҜз”ұиҝҷйҮҢе…¬ејҸдёӯзҡ„дёҖдәӣзү№дҫӢи®Ўз®—иҖҢжқҘ. йңҖиҰҒиҜҙжҳҺзҡ„жҳҜдёҚеҸӘжңүиҝҷд№ҲдёҖдәӣзү№дҫӢ, д»ҺwikipediaеҸҜд»Ҙж–№дҫҝең°жүҫеҲ°йӮЈдәӣеӨҚжқӮзҡ„жЁЎжқҝжҜ”еҰӮеғҸ:
Sample Gaussian matrix
This is a sample matrix, produced by sampling the Gaussian filter kernel (with Пғ = 0.84089642) at the midpoints of each pixel and then normalising. Note that the center element (at [4, 4]) has the largest value, decreasing symmetrically as distance from the center increases.
| 0.00000067 | 0.00002292 | 0.00019117 | 0.00038771 | 0.00019117 | 0.00002292 | 0.00000067 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00002292 | 0.00078633 | 0.00655965 | 0.01330373 | 0.00655965 | 0.00078633 | 0.00002292 |
| 0.00019117 | 0.00655965 | 0.05472157 | 0.11098164 | 0.05472157 | 0.00655965 | 0.00019117 |
| 0.00038771 | 0.01330373 | 0.11098164 | 0.22508352 | 0.11098164 | 0.01330373 | 0.00038771 |
| 0.00019117 | 0.00655965 | 0.05472157 | 0.11098164 | 0.05472157 | 0.00655965 | 0.00019117 |
| 0.00002292 | 0.00078633 | 0.00655965 | 0.01330373 | 0.00655965 | 0.00078633 | 0.00002292 |
| 0.00000067 | 0.00002292 | 0.00019117 | 0.00038771 | 0.00019117 | 0.00002292 | 0.00000067 |
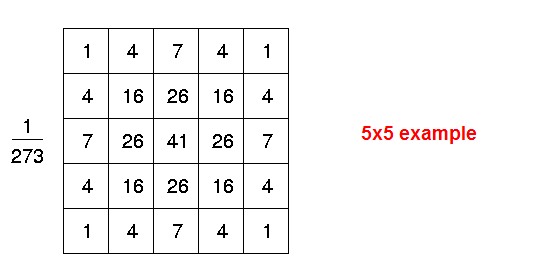
жҳҜдёҚжҳҜзңӢеҲ°е°ұеӨҙеӨ§дәҶпјҹдёҚиҝҮжІЎе…ізі», еҜ№дәҺдёҖиҲ¬зҡ„еә”з”ЁжқҘиҜҙ, еүҚйқўзҡ„дҫӢеӯҗе·Із»ҸеҸҜд»Ҙе®ҢжҲҗд»»еҠЎдәҶ.В д»Јз Ғзҡ„иҜқжҲ‘们иҝҳжҳҜз»ҷдёҖд»Ҫ5x5зҡ„example:
<span style="font-size:12px;">void gaussianFilter2 (unsigned char* corrupted, unsigned char* smooth, int width, int height)
{
int templates[25] = { 1, 4, 7, 4, 1,
4, 16, 26, 16, 4,
7, 26, 41, 26, 7,
4, 16, 26, 16, 4,
1, 4, 7, 4, 1 }; //ж»ӨжіўеҷЁжЁЎжқҝ
memcpy ( smooth, corrupted, width*height*sizeof(unsigned char) ); //еӨҚеҲ¶еғҸзҙ
for (int j=2;j<height-2;j++) //иҫ№зјҳдёҚеӨ„зҗҶ
{
for (int i=2;i<width-2;i++)
{
int sum = 0;
int index = 0;
for ( int m=j-2; m<j+3; m++)
{
for (int n=i-2; n<i+3; n++)
{
sum += corrupted [ m*width + n] * templates[index++] ;
}
}
sum /= 273;
if (sum > 255)
sum = 255;
smooth [ j*width+i ] = sum;
}
}
} </span>
еҸӮиҖғиө„жәҗпјҡ

