通过一个实例来看看如何控制wxPython的输出,并观察各必要对象的创建次序及生命周期。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Function:简单的wxPython程序
Input:NONE
Output: NONE
author: socrates
blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/dyx1024/
date:2012-07-01
"""
import sys
import wx
class MyFrame(wx.Frame):
"""
创建一个Frame类
"""
def __init__(self, parent, id, title):
print u"Frame对象初始化(Frame _init__)"
wx.Frame.__init__(self, parent, id, title)
class MyApp(wx.App):
"""
创建一个App类
"""
def __init__(self, redirect = True, filename = None):
print "APP __init__"
wx.App.__init__(self, redirect, filename)
def OnInit(self):
print u"APP对象的OnInit方法(OnInit)"
self.frame = MyFrame(parent = None, id = -1, title = u"测试wxPyhont输出重定向")
self.frame.Show()
self.SetTopWindow(self.frame)
print >> sys.stderr, u"输出到标准错误控制台。"
return True
def OnExit(self):
print u"APP对象的OnExit方法"
def main():
app = MyApp(redirect = True) #开始重定向
print u"begin MainLoop"
app.MainLoop()
print u"after MainLoop"
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
运行一下看看:
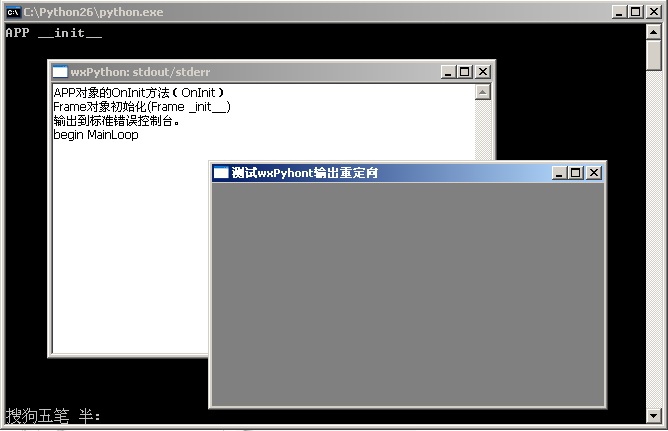
可见,在APP对象创建之后(init方法调用结束),由于指定了重定向功能,所以输出切换到了stdout/stderr。
由上面的输出也可以看到各对象的生命同周期,创建先后顺序:
- app.init()
- app.OnInit()
- Frame._init()
- app.MainLoop()
- app.OnExit()
观察这一句:app = MyApp(redirect = True) #开始重定向:
- 当redirect为True时,输出到wxPython框架,此时也可启用filename来指定输出到文件。
- 当redirect为False时,输出到控制台。